 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 2-1. Neutron Flux Densities to be Regarded as Equivalent to a Radiation Level of 1 Millirem per Hour (mrem/h) * |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
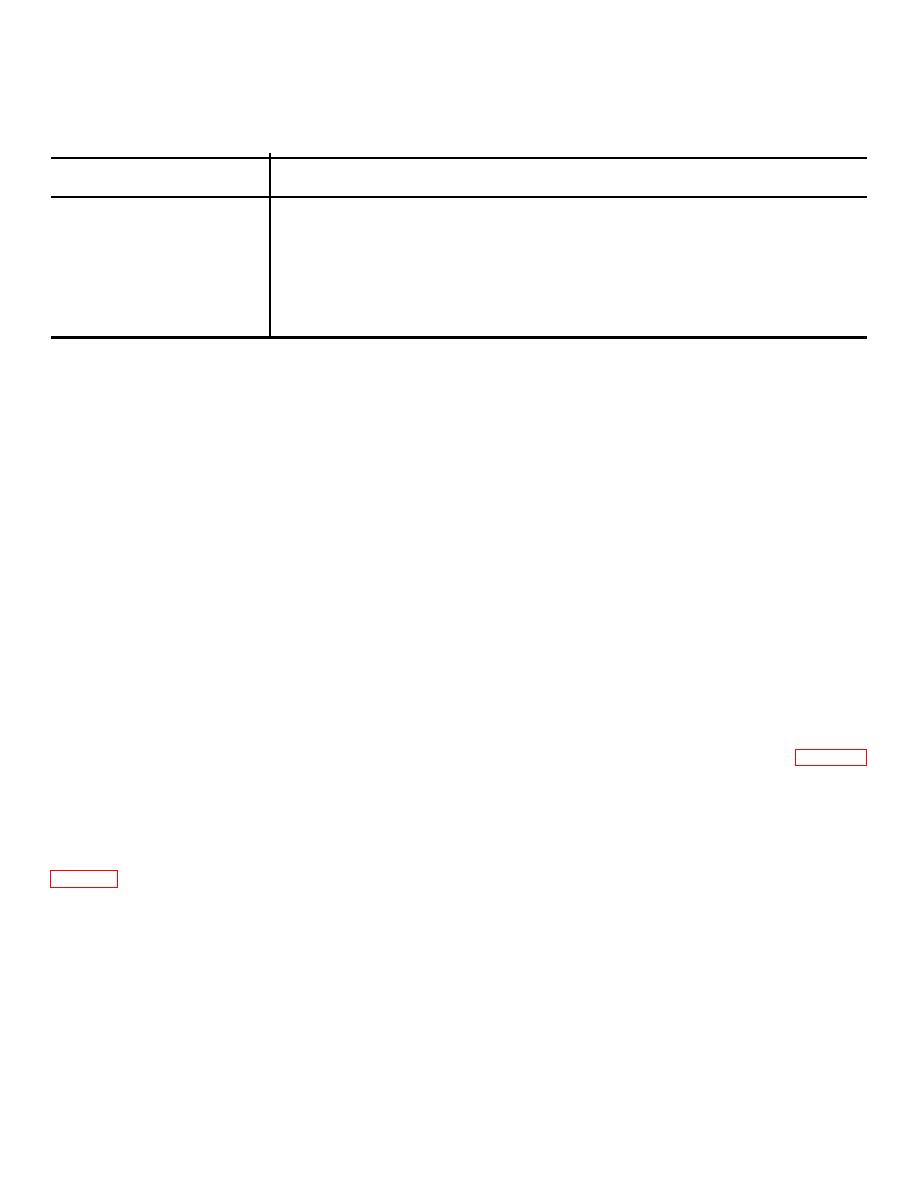 TM 55-315
Table 2-1. Neutron Flux Densities to be Regarded as Equivalent to a Radiation Level of 1 Millirem per Hour
(mrem/h) *
Flux density equivalent to 1 mrem/h (Neutrons per square
centimeter per second) (n/cm2/s)
Energy of neutron
Thermal
268.0
5 keV
228.0
20 keV
112.0
100 keV
32.0
500 keV
12.0
1 MeV
7.2
5 MeV
7.2
10 MeV
6.8
* Flux densities equivalent for energies between those listed above may be obtained by linear interpolation.
c. Gamma Radiation. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation similar to x-rays. Compared on
the basis of the same energy, gamma rays are more penetrating than alpha or beta particles.
d. Neutron Radiation. The intensity of neutron radiation is expressed in terms of "neutron flux", which is the
number of neutrons passing through a unit area in a unit time. A neutron is an uncharged particle present in all atomic
nuclei except those of light hydrogen. Compared on the basis of the same energy, neutrons are more penetrating than
beta particles and may be more or less penetrating than x-rays or gamma rays, depending upon the neutron cross
section of the interacting medium.
2-32. Radiation Units
Radiation units are indirect measures of the quantity of radiation. In this manual, radiation units are the radiation
absorbed dose (rad), roentgen (R), and roentgen equivalent man (rem).
2-33. Radioactive Article
A radioactive article is any manufactured instrument or article that has radioactive material as a component part.
2-34. Radioactive Contents
Radioactive contents are the radioactive materials, together with any contaminated liquids or gases, within the package.
2-35. Radioactive Decay Chain
A radioactive decay chain is a succession of nuclides, each of which transforms into the next until a stable nuclide is
formed. The first member of the series is called the parent, the intermediate members are called the daughters, and the
final member is called the end product.
2-36. Radioactive Material
Radioactive material is any material with a specific activity greater than 0.002 microcurie per gram (uCi/g) (see para 2-43
below).
2-37. Radionuclide
A radionuclide is a species of atom, characterized by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus, that exhibits the
property of radioactivity.
2-38. Radionuclides, A1 and A2 Values
2-39. Roentgen (R)
A roentgen is that quantity of X or gamma radiation that will produce, as a result of ionization, one electrostatic unit of
electricity, of either sign, in 1cc of dry air at 0 and standard atmosphere pressure. The mass of 1cc of dry air under the
C
standard conditions specified is 0.001293 gram. One roentgen is equivalent to energy absorption of 86.9 ergs per gram
in air. A milliroentgen (mR) is one-thousandth (10-3) of a roentgen.
2-40. Roentgen Equivalent Man (rem)
The rem is a measure of the dose of any ionizing radiation to body tissue in terms of its estimated biological effect
relative to a dose of one roentgen of x-rays. (One millirem (mrem) equals one-thousandth (10-3) of a rem.) The relations
of the rem to other dose units depend on the biological effect under consideration and the conditions of irradiation. For
this manual, any of the following is considered to equal a dose of 1 rem.
2-4
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |